Grid-Interactive Efficient Buildings (GEBs)
What is a GEB?
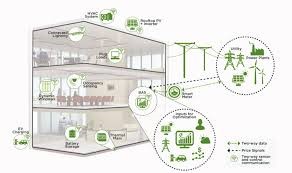
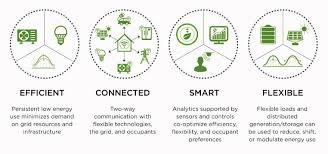
Images source: US Department of Energy
A Grid-interactive Efficient Building (GEB) is a building that integrates and continuously utilizes Distributed Energy Resources (DERs) for the benefit of building owners and occupants, as well as the grid. A GEB uses analytics and controls to optimize energy use for occupant patterns and preferences, utility price signals, weather forecasts and available on-site generation and storage. To take full advantage of the technology used in a GEB, it should also have a very energy-efficient building envelope. GEB as a concept is still new; many states are still in the first stages of managing their building energy holistically. However, there are currently many technologies being deployed, researched and developed that support the GEB concept.
Energy Efficiency Programs and GEB
Energy efficiency programs are critical to reducing the considerable energy consumption and carbon emissions in the buildings sector. GEB-related technologies can significantly reduce that consumption. Deployable technologies include, but are not limited to, the following:
- High-efficiency lighting devices
- Smart appliances
- High-efficiency heat pumps
- Thermal storage
- Dynamic glazing
- Advanced sensors and controls
- Software for optimizing building design and operation
- Interoperable building communication systems
Status of GEBs in the Midwest
In 2019, MEEA conducted research for US DOE on Grid-interactive Efficient Buildings (GEB) in the Midwest. MEEA found that GEB-related technologies are currently being deployed as part of energy efficiency and load management programs run by many utilities, and some have ongoing or completed stakeholder meetings to identify pathways for a modernized grid. MEEA continues to engage our members and other stakeholders on policies, programs and projects that advance GEBs in our region through our Building Policy Team.